featured Dystonia
On by ZimSeller Pharmacy 0 comments
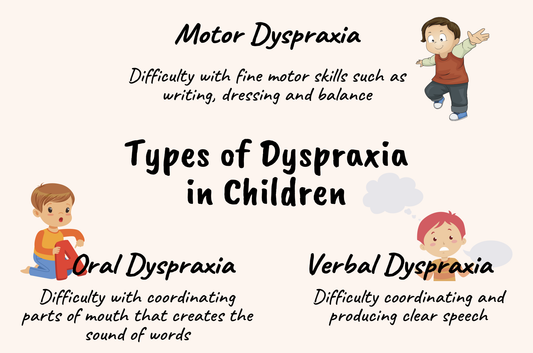
Dyspraxia in children
On by ZimSeller Pharmacy 0 comments
Dyspraxia (developmental co-ordination disorder) in adults
On by ZimSeller Pharmacy 0 comments
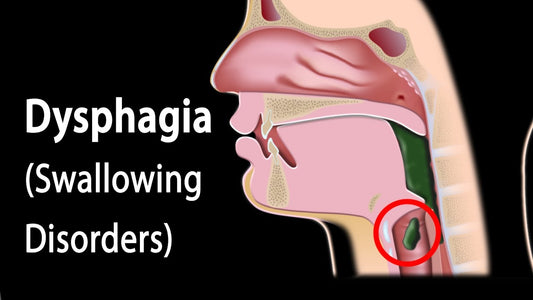
Dysphagia (swallowing problems)
On by ZimSeller Pharmacy 0 comments
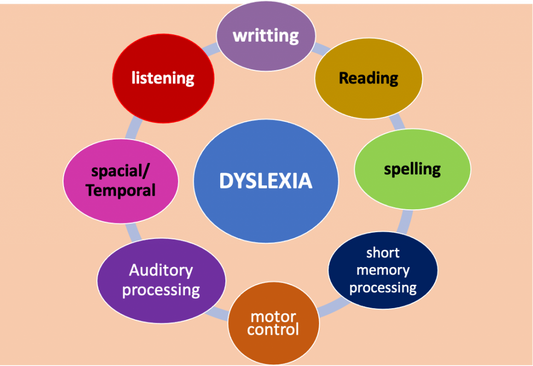
Dyslexia
On by ZimSeller Pharmacy 0 comments
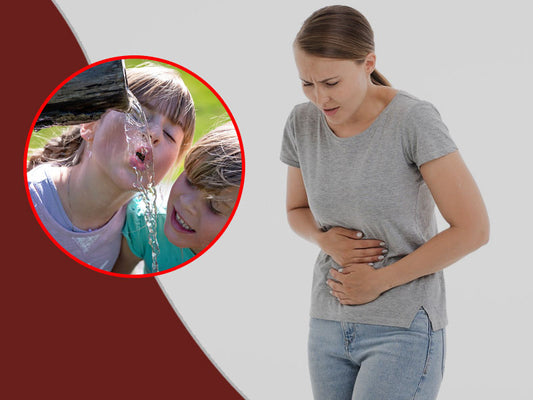
Dysentery
On by ZimSeller Pharmacy 0 comments
Dysarthria (difficulty speaking)
On by ZimSeller Pharmacy 0 comments