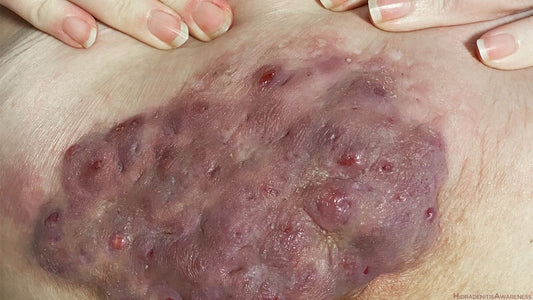
featured Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS)
On by ZimSeller Pharmacy 0 comments
Hiccups
On by ZimSeller Pharmacy 0 comments
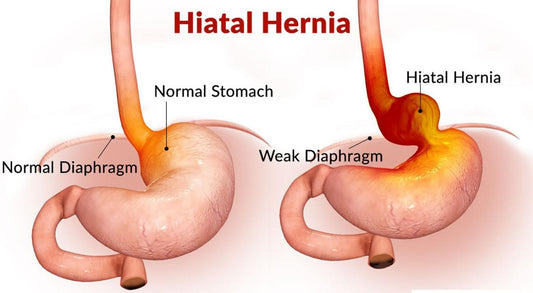
Hiatus hernia
On by ZimSeller Pharmacy 0 comments
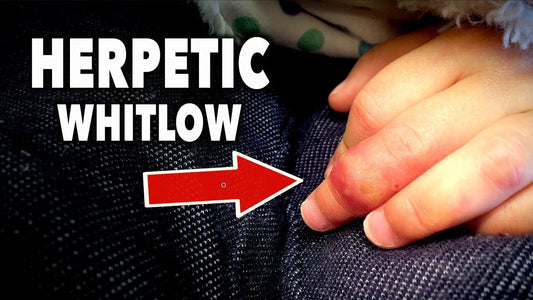
Herpetic whitlow (whitlow finger)
On by ZimSeller Pharmacy 0 comments
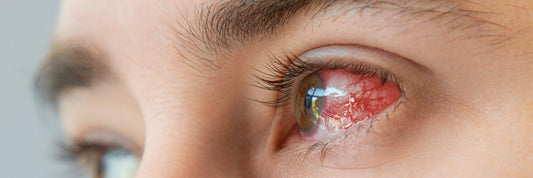
Herpes simplex eye infections
On by ZimSeller Pharmacy 0 comments
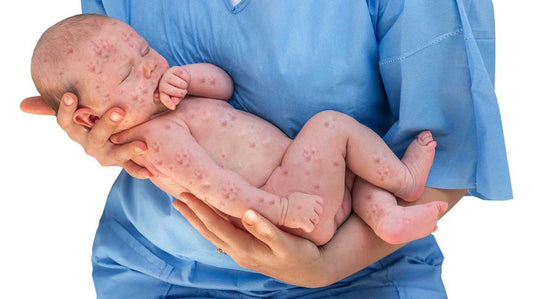
Herpes in babies
On by ZimSeller Pharmacy 0 comments
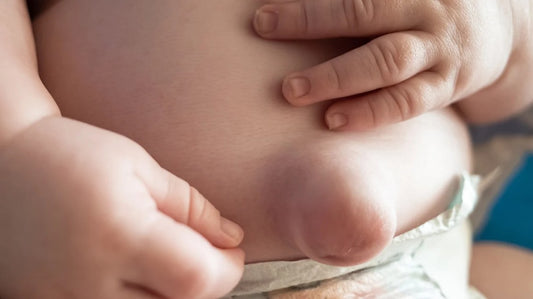
Hernia (umbilical)
On by ZimSeller Pharmacy 0 comments