featured Hearing voices
On by ZimSeller Pharmacy 0 comments
Hearing tests for children
On by ZimSeller Pharmacy 0 comments
Hearing tests
On by ZimSeller Pharmacy 0 comments
Hearing loss
On by ZimSeller Pharmacy 0 comments
Health anxiety
On by ZimSeller Pharmacy 0 comments
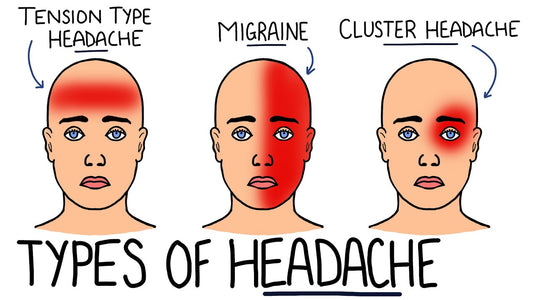
Headaches in children
On by ZimSeller Pharmacy 0 comments
Headaches (tension-type)
On by ZimSeller Pharmacy 0 comments