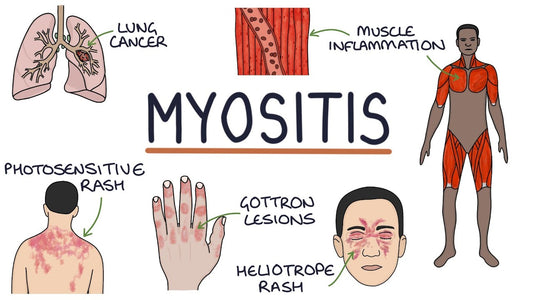
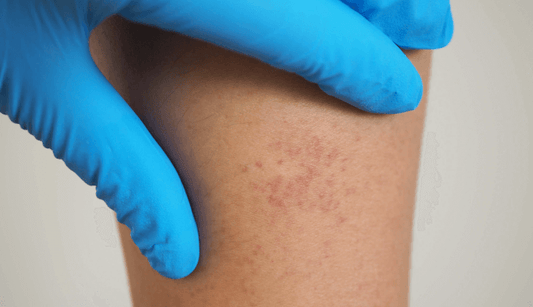
featured Myositis (polymyositis and dermatomyositis)
On by ZimSeller Pharmacy 0 comments
Myopia
On by ZimSeller Pharmacy 0 comments
Myeloma
On by ZimSeller Pharmacy 0 comments
Myelodysplastic syndrome (myelodysplasia)
On by ZimSeller Pharmacy 0 comments
Mycobacterium chimaera infection
On by ZimSeller Pharmacy 0 comments
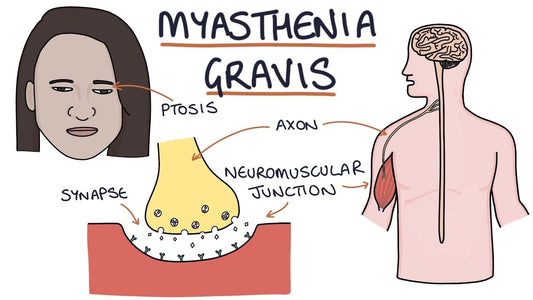
Myasthenia gravis
On by ZimSeller Pharmacy 0 comments
Myalgic encephalomyelitis (ME)
On by ZimSeller Pharmacy 0 comments