featured Molluscum contagiosum
On by ZimSeller Pharmacy 0 comments
Moles
On by ZimSeller Pharmacy 0 comments
Molar pregnancy
On by ZimSeller Pharmacy 0 comments
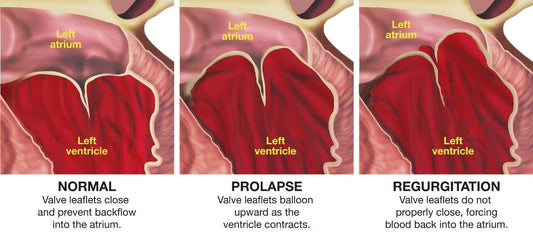
Mitral valve problems
On by ZimSeller Pharmacy 0 comments
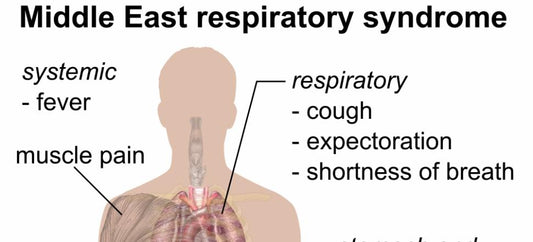
Middle East respiratory syndrome (MERS)
On by ZimSeller Pharmacy 0 comments
Metallic taste
On by ZimSeller Pharmacy 0 comments
Metabolic syndrome
On by ZimSeller Pharmacy 0 comments